BACKGROUND
Contrary to what many people think, photovoltaic energy is not an invention of the 20th century !
It was the French physicist, Antoine Becquerel, who discovered the photovoltaic effect in 1839, when he was observing the electric behaviour of electrons in a liquid. And it was only more than a century later, in 1954, that three American researchers – Chapin, Pearson and Prince – developed a silicon photovoltaic cell in the laboratories of the Bell Telephone company.
The scientists foresaw the possibility of producing electricity with these cells…


1958 Launch into orbit of the first satellites equipped with solar panels.
1973 Construction of the first house powered by photovoltaic panels at the University of Delaware.
1980-2000 Photovoltaic continues apace with the building of many power plants and many low-power products such as watches, calculators, radio and weather beacons, pumps, etc.
1995 The first programmes of photovoltaic roofs connected to the power grid are launched in Japan and in Germany. They become widespread in the early 2000s.
Depuis 2000… Photovoltaic systems are part of the sustainable development movement and allow access to a source of clean energy for all.
PHOTOVOLTAIC TECHNOLOGY
How does it work ?
Photovoltaic technology is based on cells which convert the sun’s rays into direct electric current. These cells are linked together to form a module, itself connected to various electronic components (inverter, connection box, etc.). Together they comprise a photovoltaic system. A module has a guaranteed 25-year lifetime.
Important point: a photovoltaic module does not undergo any mechanical wear.
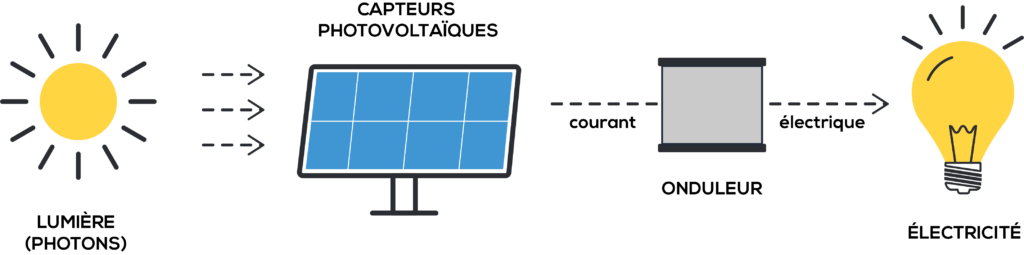
The electric current produced can be consumed on the spot, this is self-consumption, or injected into the public grid.
